TANSEL TERCAN
(PhD.Student, L.N. Gumilyov Eurasian National University, Kazakhstan & Rixos President Astana, General Manager, tansel.tercan@rixos.com)
Abstract
The main purpose of study is to examine the researches published in the field of waste management and recycling in tourism science at the period of 1980-2019 with bibliometric perspective and to determine the waste management research area trends in this discipline in the last 39 years. In this context, the Web of Science database was searched under the title of waste management and recycling within the scope of ‘hospitality, leisure and tourism’. In the research, number of publications, publication languages, types of publications, journal co- citation network, author co-citation network, document co-citation network and co-occurring author keywords were analyzed. Social network analysis was used to test purposes. According to the results, it can be said that interest in the field in the context of waste management in tourism publications has increased significantly since 2018. Studies are mainly articles. According to the results, it can be said that Gosling is a pioneer in both waste management and recycling in tourism science. If found that the most commonly used keywords in waste management are sustainability, tourism and food waste. It is determined that the most used words in the field of recycling are tourism, heritage and green hotel.
Keywords: Waste management, recycling, social network analysis, bibliometric.
INTRODUCTION
Sustainable tourism aims to achieve the best balance between economic benefits and social and environmental costs. Mow forth and Munt (1998) found that the growth of mass tourism has led to a series of problems that have become more apparent in recent years. Perhaps the most important of these is environmental problems. Usually plastic, metal, glass, paper and food etc. in hotels are wastes. Sorting and sorting them for recycling; the protection of the natural environment and the evaluation of these wastes by local administrations are of great importance especially for SMEs. In addition, since water and energy use are interconnected, water management in a hotel is not separated from energy management. The total monthly laundry load, the total number of customers per month and the total number of monthly food services affect the total monthly water and energy consumption of the hotel. Therefore, environmentally friendly machinery and equipment used in the hotel means both water and energy saving (Emeksiz, 2007).
One of the sectors where food waste (Owen et al., 2013), which has an important place among the wastes occurring in the tourism sector, is intensively formed is the food and beverage business (Creedon et al., 2010). As it is known, food and beverage enterprises can be independent enterprises or they can also serve in hotels as in hotels (Öztaş, 2002). Accordingto Crosby (1993), food waste has a significant share in other wastes occurring in hotels. In the 1990s, the responses of hotel enterprises to the programs to reduce solid waste were negative. Because of the labor costs and equipment costs, the company is believed to incur additional costs (Wilco et al., 2001). In fact, we can say that in terms of hotel operations, solid waste management and recycling are beneficial both in terms of the hotel’s monetary activities and the reduction of environmental pollution in terms of sustainability of tourism and the health of the surrounding community (Shamshiry et al., 2011).
Academic researches on waste management and recycling gained momentum, when the importance of waste management in the tourism industry was realized. Nowadays, waste management and recycling in tourism science is still considered as a current issue. It is thought that bibliometric analysis of waste management studies from past to present will be guiding for future studies. Bibliometric analysis is conceptualized as the application of mathematical and statistical methods to publications (Pritchard, 1969). In bibliometric researches, certain features of documents or publications are included in The Analyzes and some findings related to scientific networks are revealed (Al and Coştur, 2007). Bibliometric research makes it possible to determine the trends in the field by analyzing the literature in a certain field quantitatively and examining the discovered words (Kasemodel et al., 2016). Thus, with bibliometric analysis, authors, countries, sources, etc., which direct scientific publications in the field, road map can be presented to researchers (Aydın, 2014).
In bibliometric research, one of The Analyzes used for examining academic-cooperation and common-citation-relationships is social network analysis. Social network analysis is one of the first methods used to visualize collaboration and common-citation-networks and to identify information networks that are effective in the development of research area (Karagöz and Yüncü, 2013). The most important data sources in bibliometric research are the Scientific Citation Index (SCI), Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) and Art & Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI). It is possible to access these indexes and all materials of these publications through the Web of Science Core Colection database. The Web of Science (WoS) contributes significantly to bibliometric research as a database covering bibliometric data related to academic scientific publications scanned in these indexes. In this context, the studies dealing with waste management and recycling in WoS database have been examined for the purpose of this study.
BIBLIOMETRIC RESEARCHES ON WASTE MANAGEMENT AND RECYCLING
Bibliometric analysis allows examining the features of the researches carried out on certain subjects such as subject, sample, citation, word, scope. In the field of tourism, bibliometric analysis has increased in recent years. It can be said that the bibliometric analyzes researches in the literature are examined the articles published in journals, conference papers and theses. As a result of the literature review, it can be said that bibliometric analyzes on waste management and recycling in tourism area are limited.
Day and Cai (2012) examined the relationship between tourism, energy and environment. This research approached tourism as a complex system adapted from consumers, transport providers, travel agents, destinations, tourism-related multiple companies and other stakeholder groups. The challenges that arise with the addition of environmental and energy- related components to the system that forms a whole as enterprises and individuals are examined in various units. For this purpose, a total of 92 articles on energy and tourism between 1974 and 2011 were reviewed. At the same time, the effects of the social and cultural differences of the United States and China on environmental and energy-related issues are addressed. As a result of the research, suggestions have been made for problems related to the problems such as building system capacity, technology development and adaptation, supporting behavior change of individuals, understanding of the balances and interactions within the system and adopting multidisciplinary approaches to these difficulties in the tourism system.
Arslan and Emeksiz (2016) compiled national and international study conducted in the topic of environmental management in literature. They have conducted a bibliometric analysis on environmental management studies in terms of both national and international aspect. It has been found that articles on environmental management in tourism concentrate on the protection of environmental assets and the use of renewable resource. Mota et al. (2018) conducted a study to reveal research trends linked to the keywords, specific needs and respective gaps for future scientific research within the research field of tourism planning and sustainable development. They create visualization maps of the intellectual structure for a systematic review of the literature by using VOSviewer Software and applying bibliometric techniques. They used articles published and annual citations for the period 1997 to 2017 of the WoS database for
purpose of study. The results draw attention to multiple research clusters focused on the intellectual structure of tourism planning and sustainable development (Muta et al., 2018).
Garrigos-Simon et al. (2018) have done a research that aims to present a bibliometric result of tourism sustainability research, and tourism sustainability related to employment and income. In their work, they analyzed 2279 references collected from WoS Collection database and used the visualization of similarities VOSviewer program to graphically map the material. They used co-occurrence of keywords, bibliographic coupling, co-citation and co-authorship analyses. The co-authorship analysis of tourism sustainability revealed the prevalence of four countries (the USA, Australia, Spain, and England), leading the main clusters (Garrigos-Simon et al., 2018).
Ninerola et al. (2019) conducted a study to use a bibliometric approach to review the sustainability literature in tourism. Bibliometric indicators, such as citations, are used to identify the field structure and the VOSviewer software is used to map the main trends in this area. They found over the period 1987–2018, a total of 4647 papers were in Scopus regarding sustainability issues in tourism. Analysis of the leading journals, authors, institutions, and keywords indicates that the literature on sustainability issues in the field of tourism is significantly growing and a mere six papers accounted more than 300 citations, but there are several prolific authors.
METHODOLOGY
In order to determine the bibliometric characteristics of the researches published in the field of waste management and recycling in tourism science, 24 researches about waste management and 31 researches about recycling published between 1980-2019 years and indexed in the Web of Science (WoS) database were examined. “Waste management” and“recycling” terms were searched in the Web of Science Core Collection database under the sub- theme of Hospitality, Leisure and Tourism. The publication years, publication languages, types of publications, author names, titles, authors’ countries, how many references they refer and citations, abstracts, keywords and bibliography information were accessed and downloaded.
Within the scope of the data obtained, firstly the distribution of researches in terms of characteristics, publication languages, the source country of the publication and the types of publication were examined (waste management and recycling researches are separately examined). In the context of citation analysis, the source of the research conducted in the field of waste management and recycling, the citations they received scanned in the WoS database and their distribution by publications and years were examined. Social network analysis was used to determine The journal co-citation network, author co-citation network, document co- citation network and co-occurring author keyword. Citespace II application was used in social
network analysis. The data of researches in the WoS database were uploaded to the Citespace II program and analyzed. Citespace II is a Java application used to visualize and analyze emerging trends and trends in academic literature (Chen et al., 2010).
Modularity and average silhouette values of the network were calculated with the analysis performed (Al and Doğan, 2012). The modularity value determines whether any network can be divided into independent clusters and takes a value between “0” and “1”. A low modularity refers to a network that cannot be reduced to clusters with clear boundaries, while a high modularity means a well structured network (Chen et al., 2010). The average silhouette value is between [(-1) and (1)] (Chen et al., 2010) and is used to determine the maximum number of clusters, the value is greater than 0.7 indicates a strong cluster (Simovici, 2007).
The research was carried out according to the centrality values of the journal co-citation network, author co-citation network, document co-citation network and co-occurring author keywords in the network. The centrality value indicates the level of connection a node has to other nodes that are not connected to each other. The high centrality value of a node indicates that it is a bridge connecting other nodes (Ni et al. 2017). Citation burst of the journal co-citation network were also calculated in the study. The explosion indicates whether a given frequency has statistically significant fluctuations over a short period of time in the total year period (Chen et al., 2010).
RESULTS
Distribution of Publications
The distribution percentages of the number of publications used in the study are given in Table 1 on the basis of years.
Table 1: Distribution of Publications by Years
| Years | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 6 | 25 |
| 2018 | 4 | 16.6 |
| 2017 | 3 | 12.5 |
| 2016 | 3 | 12.5 |
| 2015 | 2 | 8.3 |
| 2014 | 1 | 4.2 |
| 2012 | 2 | 8.3 |
| 2011 | 1 | 4.2 |
| 2007 | 1 | 4.2 |
| 1997 | 1 | 4.2 |
| Total | 24 | 100 |
| Years | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2 | 6.5 |
| 2018 | 6 | 19.3 |
| 2017 | 3 | 9.7 |
| 2016 | 5 | 16.1 |
| 2015 | 4 | 12.8 |
| 2014 | 2 | 6.5 |
| 2013 | 1 | 3.2 |
| 2012 | 2 | 6.5 |
| 2011 | 3 | 9.7 |
| 2010 | 2 | 6.5 |
| 2008 | 1 | 3.2 |
| Total | 31 | 100 |
24 publications in waste management for the years 1997-2019 and 31 publications in recycling for the years 2008-2019 were published. The most publications on waste management were published in 2019 with 6 publications. When analyzed on the basis of years, most publications related to recycling were published 2018 with 6 publications. The types of publications for the years 2008-2019 are given in Table 2.
Table 2: Distribution by Type of Publication
| Years | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Article | 20 | 83.3 |
| Proceedings Paper | 4 | 16.7 |
| Book Chapter | 1 | 4.2 |
| Review | 1 | 4.2 |
| Total | 26 |
| Years | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Article | 27 | 87.1 |
| Proceedings Paper | 5 | 16.1 |
| Book Chapter | 4 | 12.9 |
| Review | 1 | 3.2 |
| Total | 37 |
There are 4 types of publications. It has been determined that the most published publication type is the article. The conference proceedings and the book section follow the article. The reason why the total number of publication types is higher than the distribution of publications according to the years in Table 1 is that some publications are considered to be more than one publication type in the Web of Science database. Among publications, article- type publications are the most weighted.
The waste management publications examined in the study referred to a total of 208 sources. These 24 studies have received a total of 199 citations by other studies. Five of these citations consist of citations made by the authors. The average number of citations per publication is 8.67, while the h-index is 8. Therefore, it can be said that there are 8 publications with at least 8 citations on waste management in tourism. Recycling publications examined within the scope of the study referred to a total of 317 sources. These 31 studies received a total
of 307 citations by other studies. Three of these citations are made by the authors themselves. The average number of citations per publication is 10.23, while the h-index is 8. Therefore, it can be said that there are 8 publications with at least 8 citations on recycling in tourism.
The 23 of the publications on waste management were written in English and 1 in Spanish. When the countries in which waste management publications are made are examined, it is determined that 6 publications which correspond to %25 of the publications are originated from England. The England is followed by America with 4 publications, China with 2 publications and United Arab Emirates with 2 publications. Other countries publish 1 publication are Australia, Botswana, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada and Croatia. All publications related to recycling are written in English. When the countries where recycling publications are made are examined, it is determined that 8 publications corresponding to %26 are from Australia. Australia is followed by England with 5 publications, America with 4 publications, Malaysia with 3 publications, Korea with 3 publications, Italy with 2 publications, Norway with 2 publications and China with 2 publications. Other countries publish 1 publication are Botswana, Czech Republic, Germany, Greece and Netherlands.
Journal Co-citation Network
As a result of the social network analysis carried out in order to determine the journals in which the publications have common references and important publications in the field of waste management and recycling, the names of the journals according to their degree of centrality are given in Figure 1.


Figure 1: Journal Co-citation Network by Degree of Centrality
According to the results of waste management, it is determined that there is a journal co-citation network consisting of 68 nodes and 159 connections. The resulting network consists of a total of 16 clusters. The density of the network is 0.069. The modularity value of the obtained network was calculated as Q = 0.76 and the mean value of silhouette as 0.62. According to the results of recycling, it is determined that there is a journal co-citation network consisting of 63 nodes and 190 connections. The resulting network consists of a total of 13 clusters. The density of the network is 0.097. The modularity value of the obtained network was calculated as Q = 0.58 and the mean value of silhouette as 0.63. The size and thickness of the pink circles around the nodes indicate that the degree of centrality of the nodes is higher than that of the other nodes (Ukşul, 2016).
Table 3 summarizes the network values of the top 5 journals, which have an important place in networks. According to the results of waste management, the International Journal of Hospitality Management, with 26 citations, is the most frequently cited journal of waste management research. This journal is followed by Tourism Management with 12 citations and Journal of Cleaner Production with 10 citations. According to the results of recycling, the Journal of Sustainable Tourism, with 35 citations, is the most frequently cited journal in the field of recycling research. This journal is followed by Tourism Management with 21 citations and Annal of Tourism Research with 19 citations.
| Journal | F | Year | #Cluster |
| Waste Managemet | |||
| International Journal of Hospitality Management | 26 | 2012 | 0 |
| Tourism Management | 12 | 2017 | 0 |
| Journal of Cleaner Prodution | 10 | 2017 | 0 |
| Journal of Sustainable Tourism | 8 | 2018 | 0 |
| Internation Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Manag. | 7 | 2018 | 0 |
| Recycling | |||
| Journal of Sustainable Tourism | 35 | 2010 | 0 |
| Tourism Management | 21 | 2010 | 0 |
| Annal of Tourism Research | 19 | 2010 | 1 |
| International Journal of Hospitality Management | 12 | 2015 | 0 |
| Journal of Travel Research | 8 | 2010 | 1 |
The mean of centralizing the network in Figure 2 is that most of the current research on waste management and recycling generally refers to current research. The bursting values of waste management journals according to years are given in Table 4.
| Dergi | Başlangıç | Bitiş | Patlama | 1996-2019 |
| Int. Journal of Hospitality Manag. | 2015 | 2019 | 3.817 |
When Table 4 is examined, it is seen that the journal with citation burst (3.81) is International Journal of Hospitality Management between years 1996-2019. According to the findings, it can be said that the studies related to waste management issues generally refer to the studies published in the International Journal of Hospitality Management. Regarding recycling, it was determined that no journal had a citation burst.
Author Co-citation Network
As a result of the social network analysis performed to determine the co-citation network, the names of the authors according to their degree of centrality are given in Figure 2. According to the results of waste management, it is determined that there is an author co-citation network consisting of 82 nodes and 169 connections. The resulting network consists of a total of 16 clusters. The density of the network is 0.050. The modularity value of the obtained network was calculated as Q = 0.83 and the mean silhouette value was calculated as 0.68. According to the results of recycling, it is determined that there is an author co-citation network consisting of 61 nodes and 131 connections. The resulting network consists of a total of 14 clusters. The density of the network is 0.050. The modularity value of the obtained network was calculated as Q = 0.73 and the mean silhouette value was calculated as 0.55.
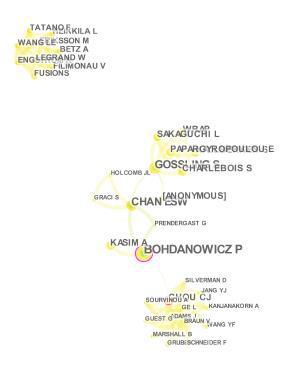
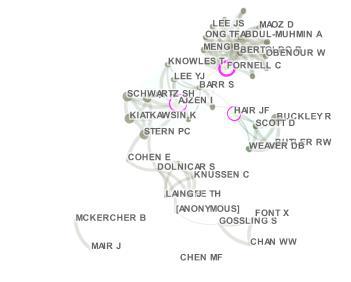
Figure 2: Author Co-citation Network by Degree of Centrality
Table 5 summarizes the network values of the top five authors of waste management and recycling separately.
| Author | F | Year | #Cluster |
| Bohdanowicz P | 8 | 2016 | 2 |
| Gossling S | 6 | 2018 | 2 |
| Chan ESW | 6 | 2017 | 2 |
| Radwan HRI | 5 | 2019 | 10 |
| Pirani SI | 5 | 2019 | 10 |
| Author | F | Year | #Cluster |
| Ajzen I | 5 | 2016 | 1 |
| Gossling S | 4 | 2014 | 5 |
| Lee TH | 4 | 2015 | 2 |
| Fornell C | 4 | 2016 | 0 |
| Buckley R | 4 | 2010 | 3 |
According to the results given in Table 5, in 24 studies published in the field of waste management, the first most cited author was Bohdanowicz with 8 citations and Gossling with 6 citations. In 31 studies published in the field of recycling, the first most cited author was Ajzen with 5 citations, while Gossling was cited with 4 citations.
Document Co-citation Network
Social network analysis was conducted in order to identify common citations of the publication. According to the results of waste management, it is determined that there is a document co-citation network consisting of 58 nodes and 116 connections. There are a total of 16 clusters. The density of the network is 0.070. The modularity value of the obtained network was calculated as Q = 0.79 and the mean silhouette value was calculated as 0.37. According to the results of recycling, it is determined that there is a document co-citation network consisting of 21 nodes and 36 connections. There are a total of 8 clusters. The density of the network is 0.171. The modularity value of the obtained network was calculated as Q = 0.45 and the mean silhouette value was calculated as 0.50. Table 6 summarizes the network values of the first five publications, which have an important place in the network.
| Publication | F | #Cluster |
| Waste Management | ||
| Pirani, SI and Arafat, HA. (2014).Solid waste management in the hospitality industry: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, 146, 320-336. | 5 | 11 |
| Papargyropoulou, E. et al. (2014). The food waste hierarchy as a framework for the management of food surplus and food waste. Journal of Cleaner Production, 76, 106- 115. | 4 | 4 |
| Pirani, SI and Arafat, HA. (2016). Reduction of food waste generation in the hospitality industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 132, 129-145. | 4 | 4 |
| Sakaguchi, L. et al (2018) Tackling the issue of food waste in restaurants: Options for measurement method, reduction and behavioral change. Journal of Cleaner Production, 180, 430-436. | 4 | 4 |
| Charlebois, S. et al. (2015). ‘Back of house’–focused study on food waste in fine dining: the case of Delish restaurants. Inte. J. Cult. Tour. Hosp. Res. 9, 278-291. | 4 | 4 |
| Recycling | ||
| Kiatkawsin, K. and Han, H. (2017). Young travelers’ intention to behave pro- environmentally: Merging the value-belief-norm theory and the expectancy theory. Tourism Management, 59, 76-88. | 3 | 7 |
| Bohdanowicz, P. et al. (2011). International hotel chains and environmental protection: an analysis of Hilton’s we care! programme (Europe, 2006–2008). Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 19, 797-816. | 2 | 4 |
| Han, H. (2015). Travelers’ pro-environmental behavior in a green lodging context: Converging value-belief-norm theory and the theory of planned behavior. Tourism Management, 47, 164-177. | 2 | 0 |
| Sanatana-Jimenez, Y. and Hernandez, J.M. (2011). Estimating the effect of overcrowding on tourist attraction: The case of Canary Islands. Tourism Management, 32, 415-425. | 2 | 0 |
| Bergin-Seers, S. and Mair, J. (2009). Emerging green tourists in Australia: their behaviours and attitude. Tourism and Hospitality Research, 9, 109-119. | 2 | 1 |
When Table 6 is analyzed, it is seen that the most cited source in the field of waste management is the article published by Pirani and Arafat in 2014. The top five current and most cited works are published by the authors Sakaguchi and Pirani-Arafat. It was determined that the most cited resource in the field of recycling was the article published by Kiatkawsin and Han in 2017. In the first five and the most cited current studies are the publications of the authors named Kiatkawsin-Han and Han.
Co-occurring Author Keywords
According to the results of the social network analysis conducted to determine the keywords of waste management research, it was determined that there is keyword network consisting of 18 nodes and 10 connections. A total of 9 clusters are available. The density of the network is 0.065. The modularity value of the obtained network was calculated as Q = 0.69 and the mean silhouette value was calculated as 0.44. According to the results of the social network analysis conducted to determine the keywords of waste management research, it was determined that there is keyword network consisting of 12 nodes and 4 connections. A total of 6 clusters are available. The density of the network is 0.078. The modularity value of the obtained network was calculated as Q = 0.78 and the mean silhouette value was calculated as 0.50. Table 7 shows the first 10 common keywords used in publications.
Table 7: Co-occurring Author Keywords Words Used in Publications
| Keywords | F | Year |
| Sustainability | 7 | 2018 |
| Tourism | 6 | 2017 |
| Food waste | 4 | 2019 |
| Hotel | 4 | 2016 |
| Reduction | 4 | 2019 |
| Solid waste | 4 | 2019 |
| Environmental management | 3 | 2019 |
| Generation | 3 | 2019 |
| Green | 3 | 2019 |
| Restaurant | 3 | 2019 |
| Keywords | F | Year |
| Tourism | 6 | 2010 |
| Heritage | 3 | 2016 |
| Green hotel | 2 | 2018 |
| Personel norm | 2 | 2018 |
| Ecotourism | 2 | 2010 |
| Perception | 2 | 2016 |
| Recycling behavior | 2 | 2016 |
| Gender | 2 | 2018 |
| Decision making | 2 | 2018 |
| Sustainable tourism | 2 | 2018 |
When Table 7 is analyzed, it is seen that the most commonly used keywords in waste management are sustainability with 7, tourism with 6 and food waste with 4. It is determined that the most used words in the field of recycling are tourism with 6, heritage with 3 and green hotel with 3.
CONCLUSION
In order to determine the bibliometric characteristics of the researches published in the field of waste management and recycling in tourism science, 24 researches about waste management and 31 researches about recycling published between 1980-2019 years and indexed in the WoS database were examined. It has been determined that there is an increase in the number of publications in waste management studies, especially in 2018, it has been determined that waste management activities have increased rapidly. Therefore, it can be said that the interest in waste management in tourism science has increased since 2018. In the context of the publication type, mostly articles were published.
The waste management publications examined in the study referred to a total of 208 sources. These 24 studies have received a total of 199 citations by other studies. The average number of citations per publication is 8.67, while the h-index is 8. Recycling publications examined within the scope of the study referred to a total of 317 sources. These 31 studies received a total of 307 citations by other studies. The average number of citations per publication is 10.23, while the h-index is 8. Most of the publications are in English.
According to the results of waste management, the International Journal of Hospitality Management, with 26 citations, is the most frequently cited journal of waste management research. According to the results of recycling, the Journal of Sustainable Tourism, with 35 citations, is the most frequently cited journal in the field of recycling research. Most of the current research on waste management and recycling generally refers to current research because these topics are emerged topics in tourism science.
In 24 studies published in the field of waste management, the first most cited author was Bohdanowicz with 8 citations and Gossling with 6 citations. In 31 studies published in the field of recycling, the first most cited author was Ajzen with 5 citations, while Gossling was cited with 4 citations. According to the results, it can be said that Gossling is a pioneer in both waste management and recycling in tourism science. It is found that the most cited source in the field of waste management is the article published by Pirani and Arafat in 2014 and the most cited resource in the field of recycling was the article published by Kiatkawsin and Han in 2017. If found that the most commonly used keywords in waste management are sustainability, tourism and food waste. It is determined that the most used words in the field of recycling are tourism, heritage and green hotel.
REFERENCES
Al, U. & Coştur, R. (2007). Bibliometric profile of Turkish Journal of Psychology. Turkish Librarianship, 21(2), 142-163.
Al, U. & Doğan, G. (2012). Citation analysis of Hacettepe University information and document management theses. Turkish Librarianship, 26(2), 349-369.
Arslan, A. & Emeksiz, M. (2016). Bibliometric profile of environmental management studies in hospitality business and recommendations for future research. Journal of Multidisiplinary Academic Tourism, 1(1), 1-12.
Aydın, B. (2014). Bibliometric analysis of the theses registered in the field of food and beverage management in the thesis center of Higher Education Council (Yöktez). In Proceedings at VII. Graduate Tourism Students Research Congress, 04-05 April 2014, Aydın, pp. 55-70.
Chen, C., Ibekwe‐SanJuan, F. & Hou, J. (2010). The structure and dynamics of cocitation clusters: A multiple‐perspective co-citation analysis. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 61(7), 1386-1409.
Creedon, M., Cunningham, D. & Hogan, J. (2010). Food waste prevention guide Ireland. Clean Technology Center, Cork Institute of Technology.
Crosby, M. A. (1993). Composting: recycling restaurant waste back to its root. Restaurants USA, pp. 10-11.
Day, J. & Cai, L. (2012). Environmental and energy related challenges to sustainable tourism in the United States and China. International Journal of Sustainable Development & World Ecology, 19(5), 379-388.
Emeksiz, M. (2007). Small hotel enterprises and environmental management. Balıkesir University Journal of Social Sciences Institute, 10(18), 141-156.
Garrigos-Simon, F. J., Narangajavana-Kaosiri, Y. & Lengua-Lengua, I. (2018). Tourism and sustainability: a bibliometric and visualization analysis. Sustainability, 10, 1976, doi:10.3390/su10061976
Karagöz, D. & Yüncü, H. R. (2013). Evaluation of research subject of doctoral theses about tourism in Turkey with social network analysis. Adıyaman University Journal of Social Sciences Institute, 6(15), 205-232.
Kasemodel, M. G. C., Makishi, F., Souza, R. C. & Silva, V. L. (2016). Following the trail of crumbs: A bibliometric study on consumer behavior in the food science and technology field. International Journal of Food Studies, 5(1), 73-83.
Mota, L., Teixeira, S. & Gonçalves, F. (2018). Remarks from tourism planning and sustainable tourism – a bibliometric study. Enlightening Tourism, A Pathmaking Journal, 8(2), 99-127.
Mowforth, M. & Munt, I. (1998). Tourism and sustainability: new tourism in the third world. London: Routledge.
Ni, C., Sugimoto, C. R. & Robbin, A. (2017). Examining the evolution of the field of public administration through a bibliometric analysis of public administration review. Public Administration Review, 77(4), 496-509.
Ninerola, A., Sanchez-Rebull, M. & Hernandez-Lara, A. (2019). Tourism research on sustainability: a bibliometric analysis. Sustainability, 11, 1377, doi:10.3390/su110513 77.
Öztaş, K. (2002). Culinary Services in Tourism Sector. Ankara: Nobel Publication.
Olcay, A., Karaçil, G. & Sürme, M. (2018). Bibliometric Profile of Halal Tourism Literature. Iğdır University Journal of Social Sciences Institute, 15, 389-408.
Owen, N., Widdowson, S. & Shields, L. (2013). Waste mapping guidance for hotels in cyprus: saving money and improving the environment. The Travel Foundation; Cyprus Sustainable Tourism Initiative.
Öztaş, K. (2002). Culinary Services in Tourism Sector. Ankara: Nobel Publication.
Pritchard, A. (1969). Statistical bibliography; an interim bibliography. North-Western Polytechnic, School of Librarianship.
Shamshiry, E., Nadi, B., BinMokhtar, M., Komoo, I., Saadiahhashim, H. & Yahaya, N. (2011). Integrated models for solid waste management in tourism regions: Langkawi Island, Malaysia. Journal of Environmental and Public Health, Article ID 709549, 1-5.
Simovici, D. (2007). Data mining algorithms I: Clustering. In Amiya, N. & Ivan, S. (Ed.), Handbook of applied algorithms (p. 177-218). New Jersey: Wiley-IEEE Press.
Ukşul, E. (2016). Evaluation of scientific publications made in measurement and evaluation in education field in Turkey with social network analysis: A bibliometric study. Unpublished Master Thesis. Akdeniz University, Education Science Institute, Antalya.
Wilco, W. & Lam, C. J. (2001). Environmental accounting of municipal solid waste originating from rooms and restaurants in the Hong Kong hotel industry. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 25(4), 371-385.